July 2025
With the shortest day now behind us and a new financial year underway, there’s fresh energy in the air and plenty to keep an eye on in the financial landscape.
Wars in Europe and the Middle East, volatile oil prices and shifting US policies are making headlines but failing to dampen the optimism of the markets.
The ASX closed the financial year with a near 10% return – its strongest since the COVID-19 crisis and despite US tariff threats.
Australia is somewhat insulated from the tariffs, but concern lingers that the federal government’s $1.5 trillion invested in the US, faces a tax hike.
The tariffs are a bigger risk for the US economy, with inflationary risks from tariffs possibly prompting rate increases. Nonetheless, Wall Street remains upbeat. The S&P 500 index surged to a four-month high in June on hopes of further rate cuts and smooth trade negotiations.
In Australia, forecasts of further interest rate cuts have fractured since tensions flared in the Middle East, with some expecting a July cut and others now tipping August.
The Aussie dollar has climbed to a seven-month high, while the US dollar tumbled to a three-year low.
Oil prices posted their sharpest weekly declines after a spike during June as the Middle East conflict reached boiling point.
Market movements and review video – July 2025
Stay up to date with what’s happened in the Australian economy and markets over the past month.
Wars in Europe and the Middle East, volatile oil prices and shifting US policies are making headlines – but failing to dampen market optimism.
The ASX closed the financial year with a near 10% return – its strongest since the COVID-19 crisis and despite US tariff threats.
Despite tariff risks for the US economy, the S&P 500 index surged to a four-month high on hopes of future rate cuts and smooth trade negotiations.
Click the video below to view our update.
Please get in touch if you’d like assistance with your personal financial situation.
Less hibernate, more activate
When the temperature drops, it feels like more of an effort, but getting outdoors, even when it’s chilly, can do your brain and body a whole lot of good.

Let’s be honest – when it’s cold outside, the couch starts to look very attractive. You’ve got the heater cranking, you’re engrossed in the latest TV series with your favourite hoodie on, and venturing out into nature seems like a job for someone far more motivated. But here’s the thing; humans weren’t designed to hibernate through winter. We’re built to get out and about and move – year-round.
Movement and exposure to natural environments – even just for short bursts – have so many health benefits. It can improve your body’s immunity, boost your mood, help you sleep better, and keep your body ticking over during the colder months.
Nature isn’t just nice – it’s medicine
It’s not just about ‘getting some fresh air’. Spending more time in nature has real, measurable effects on both the body and the brain.
A large-scale study found that spending as little as two hours a week in nature is associated with better physical health and significantly improved well-being.i That does not have to be two hours in one go – you can chip away at it over the week, whether it’s a morning stroll in a local park, a quick paddleboard, or a bit of time on the green practicing your putting.
Other studies have shown that being outdoors reduces cortisol levels (your main stress hormone), lowers blood pressure, and even enhances the overall function of your immune system. Yep – getting outside may help your body fend off seasonal bugs and colds. Exposure to natural light during the day also helps regulate your sleep cycle by supporting healthy melatonin production, so you’re more likely to sleep well and feel rested and refreshed.ii
A brain boost
It’s not just your body that benefits. Time spent outdoors has been shown to improve your mood, reduce stress and anxiety levels, and boost focus and memory.
It can also enhance the release of endorphins and dopamine, which are neurotransmitters that are associated with positive emotions, happiness, and well-being.iii
The Japanese have long understood the benefits that nature has on our mood and have a practice known as ‘shinrin-yoku’ which translates as forest bathing. This simple but powerful act of spending time in a forest became popular in the 1980’s as a response to the high stress environment of corporate Japan. So, why not try a little shinrin-yoku yourself? After all, the bush is lovely when it’s cool and crisp and the smell of a forest after rain is also something special and can create a sense of connection to nature.
You don’t have to retreat all the way to the bush for some peace and tranquillity if you are an urban dweller though. Even a quick escape into the backyard for some vitamin D can offer mental breathing room and a chance to slow down and unplug.
Move it or lose it (and not just the summer fitness)
Of course, there are real benefits to combining nature and exercise, especially during winter, which is often when our healthy routines can sometimes fall apart. The activity levels drop, the comfort food kicks in, and suddenly getting out the door requires Olympic-level motivation.
Movement – especially in natural settings – helps counteract the physical slump.
You don’t have to run a marathon. A walk along the beach, a bit of trail hiking, or hitting a few balls on the golf course is more than enough to get the heart pumping and muscles moving. Even spending 20-30 minutes outdoors can lift energy levels and help prevent the aches and stiffness that creep in during the colder months.
Worth the effort
Sure, it takes a bit more effort in winter, but nature doesn’t close for the season – and the rewards are still there if you’re willing to rug up and step out. So, whether it’s a bike ride, taking the dog for a walk or just having a potter around the garden, get out there.
And hey, the couch will still be there when you get back. Probably with a hot cuppa waiting.
i https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-44097-3
ii https://askthescientists.com/outdoors/
iii https://www.apa.org/monitor/2020/04/nurtured-nature
How to shift into pension mode
When and how you can access your super to start an account-based pension.

If our working years can be regarded as the time when we aim to build up our superannuation savings, our retirement years can equally be regarded as the time when we aim to spend them.
At least that’s the objective for most Australians. Which generally leads to the question: how do I start accessing my super funds when I do stop working, or maybe even before I stop working?
This article focuses on the basics, including the general eligibility rules around accessing your super and how to switch your super accumulation account to an account-based pension.
What age can I access my super?
To legally access your super, you generally need to have met a condition of release after turning 60-years-old.
You can do so by either stopping work completely (retiring) or by keeping working and starting a transition to retirement income stream (TRIS).
Doing so can enable you to reduce your current working hours and use your TRIS pension payments to top up your part-time income.
In either case, you have the options of turning on a pension income stream, making a lump sum cash withdrawal, or doing a combination of both.
How do I start a pension account?
Importantly, to start accessing your super, you will need to roll some or all of it over from your accumulation account into a newly created pension account.
Those starting a TRIS continue to receive compulsory super guarantee payments from their employer (which are taxed at the normal rate of 15%) into their super accumulation account. The funds held in a pension account can be accessed, however keeping in mind that investment earnings in the pre-retirement phase are also still taxed at 15%.
Most super funds offer pension account products and different investment options, similar to their accumulation account products. Those with a self-managed super fund should contact their SMSF accountant and/or speak to us to facilitate the super rollover and pension account conversion processes.
You may need to contact your super fund to find out their process, which is typically as simple as lodging a request with your fund by filling out a form and providing information such as how much of you super you want to roll over, and where to.
Once your funds are in a pension account you could then take some out as a lump sum. The Australian Tax Office (ATO) has mandated minimum annual withdrawal amounts, which depend on your age.
There is a limit on the maximum amount that can be transferred as a tax-free retirement income stream from super to a pension account, known as the transfer balance cap. This is currently set at $2 million. The ATO keeps track of how much you transfer, and if you go over the cap it will levy an excess transfer balance tax.
If you have more than $2 million in super you have the option of keeping the excess in your super account and paying up to 15% tax on your earnings, or you can withdraw the excess super as a lump sum.
What are the tax considerations in pension mode?
If you’re aged 60 or over and fully retired, any income earned on your pension assets is tax free and so are the pension payments you withdraw.
Also, a major advantage is that the profits from any investments sold within a pension account are completely capital gains tax free.
What are the minimum pension withdrawal amounts?
Once you’ve rolled over some or all of your super to an account-based pension you are required by law to withdraw a minimum pension amount each financial year, which is a percentage of your account balance based on your age.
For new pensions, the minimum withdrawal amount is calculated on a pro-rata basis from when a pension commences to the end of the financial year.
There are restrictions on how much can be withdrawn tax free through a TRIS in a financial year if you’re under 65, until you’ve met a condition of release. The minimum withdrawal amounts is 4% of your super balance and the maximum is 10%.
The table below shows the required minimum withdrawal rates if you’re in pension phase and are fully retired.
| Age on 1 July of pension commencement and on each 1 July thereafter | Minimum withdrawal amount based on pension balance for 2024/2025 |
|---|---|
| Under 65 | 4% |
| 65 to 74 | 5% |
| 75 to 79 | 6% |
| 80 to 84 | 7% |
| 85 to 89 | 9% |
| 90 to 94 | 11% |
| 95 and over | 14% |
Source: Australian Tax Office
Any amounts leftover in your pension account when you die will go to your nominated beneficiaries. Depending on the type of beneficiary (reversionary, spouse, dependant or non-dependant) the amounts can be paid as an ongoing pension stream until the account runs out or as a lump sum.
Consider getting professional advice
If you’re wanting total financial flexibility in retirement, you could consider leaving part of your money in super, rolling over some of it into an account-based pension, and also withdrawing lump sums whenever you need to.
There are a range of benefits from adopting a combination of your options, although there may also be potential tax consequences for both you and your beneficiaries.
Managing the combination of a super accumulation account, an account-based pension, an Age Pension entitlement (if eligible), potential investment earnings outside of super, and irregular lump sum payments, can be highly complex.
Using our services is a worthwhile consideration as you weigh up all of your retirement options.
This article has been reprinted with the permission of Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd. Copyright Smart Investing™
GENERAL ADVICE WARNING
Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd (ABN 72 072 881 086 / AFS Licence 227263) (VIA) is the product issuer and operator of Vanguard Personal Investor. Vanguard Super Pty Ltd (ABN 73 643 614 386 / AFS Licence 526270) (the Trustee) is the trustee and product issuer of Vanguard Super (ABN 27 923 449 966). The Trustee has contracted with VIA to provide some services for Vanguard Super. Any general advice is provided by VIA. The Trustee and VIA are both wholly owned subsidiaries of The Vanguard Group, Inc (collectively, “Vanguard”). We have not taken your or your clients’ objectives, financial situation or needs into account when preparing our website content so it may not be applicable to the particular situation you are considering. You should consider your objectives, financial situation or needs, and the disclosure documents for the product before making any investment decision. Before you make any financial decision regarding the product, you should seek professional advice from a suitably qualified adviser.You should refer to the TMD of the product before making any investment decisions. You can access our Investor Directed Portfolio Service (IDPS) Guide, Product Disclosure Statements (PDS), Prospectus and TMD at vanguard.com.au and Vanguard Super SaveSmart and TMD at vanguard.com.au/super or by calling 1300 655 101. Past performance information is given for illustrative purposes only and should not be relied upon as, and is not, an indication of future performance. Important Legal Notice – Offer not to persons outside Australia The PDS, IDPS Guide or Prospectus does not constitute an offer or invitation in any jurisdiction other than in Australia. Applications from outside Australia will not be accepted. For the avoidance of doubt, these products are not intended to be sold to US Persons as defined under Regulation S of the US federal securities laws. © 2025 Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd. All rights reserved.
How to bucket your money and save
What is bucketing your money?

Bucketing is a smart way to manage your money without complicated budgets or spreadsheets. You set up multiple bank accounts called ‘buckets’ and use each one for a specific purpose, like bills, savings or entertainment. Once your buckets are set up, it’s easier to see and control how you spend and save your money. This strategy is beneficial for anyone looking to save, reduce debt, control spending or achieve bigger financial goals. Bucketing can also help you save your money for larger but infrequent bills like car registration, school fees and energy bills.
Get started with bucketing your money
It’s easy to start bucketing and saving when you know the exact steps involved in the process.
Step 1. Work out your spending and group into categories
A good starting point is working out how you spend your money. An online expense tracker like the Spending tool, for instance, is excellent to help you see where your income goes. Next, group each category of your spending into a few themes. This could look like regular and daily expenses, emergency funds, splurge and savings. Then add up the amounts in each theme. These themes become your buckets. You can have as many buckets as you like, but here’s an example of how to group them:
Bucket 1 – Regular and daily expenses
This is for regular bills, rent, mortgage, debts, groceries, transport, school fees, insurances and holidays. This account should be linked to a debit card.
Bucket 2 – Spending or splurge money
Use this bucket for fun money to splurge on things like socialising or treating yourself and others. This account should be linked to a debit card. You can use card controls to take control of your spending.
Bucket 3 – Emergencies and safety money
This one is for the big or unexpected expenses that can catch you off guard, like home or car repairs, dental work or paying off debts. This account should earn interest and have no debit card, so you’re not tempted to spend.
Bucket 4 – Savings
Use the savings bucket to put aside money for things like travel, a new car or reducing debt. Ideally this should be an account that earns interest and has no debit card.
Step 2. Open your bucket bank accounts
To implement this financial strategy, you’ll need to get started with a basic transaction account with your bank. After you’ve opened one account, it’s easy to open or add extra savings or transaction accounts.
Learn how to open a bank account online.
Handy hints for setting up your buckets
Rename your accounts
When you open your accounts, you can name each account to match its purpose. For example, you could name them ‘Spending bucket’, ‘Fun bucket’, ‘Safety bucket’ and ‘Savings bucket’.
Step 3. Decide on your bucket amounts
This is a very important part of bucketing. The idea is money from your income ‘pours’ into each bucket in certain amounts that you decide. Ideally, all your income or wages should go into the first account, and from there you transfer money into each of your buckets.
As a guide, consider these percentages of your income for each account or bucket:
- Account 1 – Regular and daily expenses: 60%
- Account 2 – Spending money: 10%
- Account 3 – Emergencies and safety money: 10%
- Account 4 – Savings: 20%
Step 4. Set up regular deposits to your buckets
Now that you’ve worked out how much money goes into each of your accounts, you can automate transfers from your first account into the others. It’s a good idea to set up the transfers so they occur on the same day every month, soon after you get paid. This will help you avoid overspending on pay day.
Now you’re ready to start enjoying the benefits of bucketing.
Source: NAB
Reproduced with permission of National Australia Bank (‘NAB’). This article was originally published at https://www.nab.com.au/personal/life-moments/manage-money/budget-saving/money-bucket
National Australia Bank Limited. ABN 12 004 044 937 AFSL and Australian Credit Licence 230686. The information contained in this article is intended to be of a general nature only. Any advice contained in this article has been prepared without taking into account your objectives, financial situation or needs. Before acting on any advice on this website, NAB recommends that you consider whether it is appropriate for your circumstances.
© 2025 National Australia Bank Limited (“NAB”). All rights reserved.
Important:
Any information provided by the author detailed above is separate and external to our business and our Licensee. Neither our business nor our Licensee takes any responsibility for any action or any service provided by the author. Any links have been provided with permission for information purposes only and will take you to external websites, which are not connected to our company in any way. Note: Our company does not endorse and is not responsible for the accuracy of the contents/information contained within the linked site(s) accessible from this page.
Portfolios for the risk we may not be imagining
Investors have faced a wild ride in 2025. The excitement may not be over.

Equity and fixed income markets took less than a month to recover after U.S. tariff announcements in early April sent them reeling, giving investors a valuable opportunity to reexamine their relationship with risk.
A healthy relationship with risk starts with understanding that downturns aren’t always as shallow and recoveries not always as swift as we’ve seen over the last 15 years or so. Three essential principles for dealing with risk can improve outcomes even if the ride gets wilder.
Principle 1: Be humble in the face of unknowable risk
The late financial historian Peter Bernstein once observed that certain risks are inherently unknowable ahead of time. These risks tend to be the most disruptive, having the potential to befall investors without warning. For example, a key factor in the 2008 global financial crisis that became clear only with the benefit of hindsight was the amount of systemic risk that had built up via credit derivatives. The degree to which risk-taking on credit—mortgage and corporate—was concentrated within the system was not well understood until the crisis deepened. This uncertainty drove the panic that set in at the height of the crisis.
“Equity market drawdowns can run longer and deeper than we’ve become accustomed to. It’s that potentially changing landscape that investors may want to prepare for.” —Kevin Khang, Vanguard Senior International Economist
In a similar vein, what alarmed the market about the recent tariff announcements was not that new tariff policies were being pursued. Rather, it was the magnitude and scope of these policies, and the pace at which they unfolded, that had been largely unknowable and exacerbated the volatility.
Truly disruptive risk is often unknowable ahead of time. Humility regarding this truth can help investors maintain a healthy perception of risk. Accepting that unknowable risks periodically roil markets can foster a flexible and measured response when tail risks—or extreme market developments—emerge, mitigating the impact of unforeseen events and preventing panic-driven decisions.
Principle 2: Have a robust asset allocation
Because the future is uncertain, and some risks are unknowable, it makes sense to find a robust solution—one that provides results that are good enough across a range of circumstances, rather than optimal under some scenarios but highly undesirable under others. More than being balanced by some combination of stocks, bonds, and cash and diversified within each asset class, a robust portfolio is one the investor can maintain, especially in extreme market conditions.1
Rigorous capital market return projections that consider the extremes are also critical to robustness. That’s because poor long-term results are a greater risk than short-term volatility for long-term investors. In practice, a robust approach to portfolio construction considers a diverse range of return environments over the investor’s investment horizon and achieves an allocation that would be suitable across these environments.
A new book by Joe Davis, Vanguard global chief economist, provides an example of such an approach for investors with seven- to 10-year horizons. Placing the odds of the economic environment fundamentally changing over the next decade at above 80%, this approach weighs two starkly different return environments. The resulting portfolio is robust for both: 1) an optimistic environment in which AI-driven productivity drives high economic growth and market valuations; and 2) a pessimistic environment where increasing structural deficits put upward pressure on inflation and yields, while pulling down equity valuations.
Principle 3: Be optimistic but prepared for downturns
Balanced investors must thoughtfully manage downside risk. Sticking with an allocation during significant drawdowns requires realistic expectations about one’s tolerance for pain. In today’s market, this means having realistic expectations about potential drawdowns and not relying on overly optimistic return expectations based on recent performance.
Mild stock-price corrections of recent years could give way to deeper, longer-lasting declines
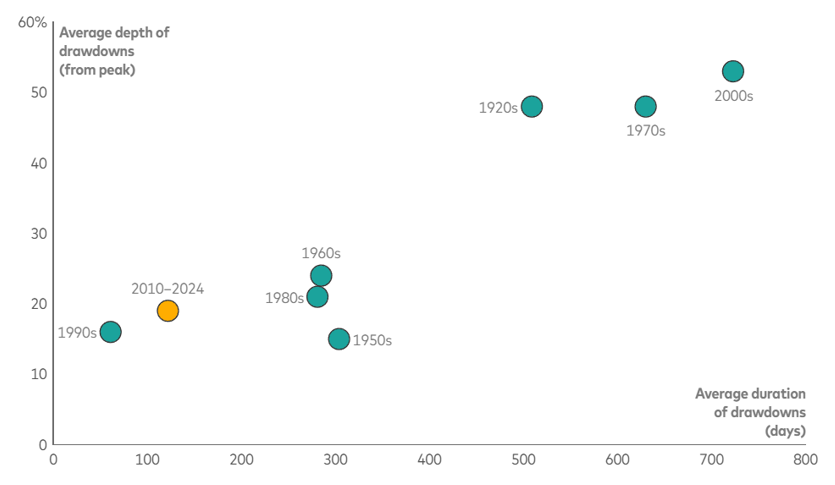
As the figure shows, the last 15 years have been favourable for U.S. equities, with shallow and short-lived drawdowns. Some investors may be tempted to look back over this period—which they consider to be “long”—and surmise that such relative market tranquility is here to stay. The quick snapback from the sharp declines after the broad U.S. tariff announcements on April 2 may only reinforce such a stance. But as we can see from previous decades, equity market drawdowns can run longer and deeper than we’ve become accustomed to recently. Looking forward, it’s that potentially changing landscape that investors may want to prepare for.
Feeling our way toward sources of future risk – and potentially recalibrating expectations
The confluence of forces that led to subdued downsides in the last 15 years may be evolving, creating a more challenging risk backdrop:
- A renewed focus on fiscal responsibility may imply a reduced scope for fiscal stimulus in future economic downturns.
- Adverse supply-side developments and the potential for stagflation might limit efforts by central banks to mitigate market volatility.
- The prospect of a rearranged global trading ecosystem has a wide range of significant long-term implications that could create sources of disruption—many of which are unknowable.
For some investors, prudent risk management might mean recalibrating expectations to include deeper and longer-lasting drawdowns that are more in line with previous historical periods. Even if this recalibration doesn’t change one’s asset allocation dramatically, it may increase the odds of the investor maintaining their allocation during downturns.
If you have any questions regarding market fluctuations, contact us today.
Notes:
All investing is subject to risk, including the possible loss of the money you invest. Be aware that fluctuations in the financial markets and other factors may cause declines in the value of your account. There is no guarantee that any particular asset allocation or mix of funds will meet your investment objectives or provide you with a given level of income. Diversification does not ensure a profit or protect against a loss.
Investments in bonds are subject to interest rate, credit, and inflation risk.
Bond funds are subject to the risk that an issuer will fail to make payments on time, and that bond prices will decline because of rising interest rates or negative perceptions of an issuer’s ability to make payments.
Investments in stocks and bonds issued by non-U.S. companies are subject to risks including country/regional risk and currency risk. These risks are especially high in emerging markets.
This article contains certain ‘forward looking’ statements. Forward looking statements, opinions and estimates provided in this article are based on assumptions and contingencies which are subject to change without notice, as are statements about market and industry trends, which are based on interpretations of current market conditions. Forward-looking statements including projections, indications or guidance on future earnings or financial position and estimates are provided as a general guide only and should not be relied upon as an indication or guarantee of future performance. There can be no assurance that actual outcomes will not differ materially from these statements. To the full extent permitted by law, Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd (ABN 72 072 881 086 AFSL 227263) and its directors, officers, employees, advisers, agents and intermediaries disclaim any obligation or undertaking to release any updates or revisions to the information to reflect any change in expectations or assumptions.
1 Some investors may wonder what’s wrong with adjusting their allocations on the fly, based on changed perceptions of risk. In some cases, the answer may be “nothing.” But such cases are likely limited to instances where market volatility has convinced the investor or their advisor that they previously over- or underestimated their risk tolerance—and that a new target mix of assets would be better for the long haul. Otherwise, Vanguard research suggests that an annual rebalancing strategy is optimal for investors who do not harvest losses for tax purposes or seek to track a benchmark. For more information, see Yu Zhang et al., Rational Rebalancing: An Analytical Approach to Multiasset Portfolio Rebalancing Decisions and Insights, Vanguard, 2022; available at corporate.vanguard.com/content/dam/corp/research/pdf/rational_rebalancing_analytical_approach_to_multiasset_portfolio_rebalancing.pdf.
This article has been reprinted with the permission of Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd. Copyright Smart Investing™
GENERAL ADVICE WARNING
Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd (ABN 72 072 881 086 / AFS Licence 227263) (VIA) is the product issuer and operator of Vanguard Personal Investor. Vanguard Super Pty Ltd (ABN 73 643 614 386 / AFS Licence 526270) (the Trustee) is the trustee and product issuer of Vanguard Super (ABN 27 923 449 966).
The Trustee has contracted with VIA to provide some services for Vanguard Super. Any general advice is provided by VIA. The Trustee and VIA are both wholly owned subsidiaries of The Vanguard Group, Inc (collectively, “Vanguard”).
We have not taken your or your clients’ objectives, financial situation or needs into account when preparing our website content so it may not be applicable to the particular situation you are considering. You should consider your objectives, financial situation or needs, and the disclosure documents for the product before making any investment decision. Before you make any financial decision regarding the product, you should seek professional advice from a suitably qualified adviser. A copy of the Target Market Determinations (TMD) for Vanguard’s financial products can be obtained on our website free of charge, which includes a description of who the financial product is appropriate for. You should refer to the TMD of the product before making any investment decisions. You can access our Investor Directed Portfolio Service (IDPS) Guide, Product Disclosure Statements (PDS), Prospectus and TMD at vanguard.com.au and Vanguard Super SaveSmart and TMD at vanguard.com.au/super or by calling 1300 655 101. Past performance information is given for illustrative purposes only and should not be relied upon as, and is not, an indication of future performance. This website was prepared in good faith and we accept no liability for any errors or omissions.
Important Legal Notice – Offer not to persons outside Australia
The PDS, IDPS Guide or Prospectus does not constitute an offer or invitation in any jurisdiction other than in Australia. Applications from outside Australia will not be accepted. For the avoidance of doubt, these products are not intended to be sold to US Persons as defined under Regulation S of the US federal securities laws.
© 2025 Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd. All rights reserved.

